- If you are a new trader, you've probably been wondering who are forex brokers, what they do and why we need them. We tell you all these here.
Forex, or the foreign currency market, is the biggest and most liquid financial market in the world. Every day, trillions of dollars are traded on it. For most people, navigating through this busy market isn’t easy. Instead, they need to go via a very important middleman: a forex broker. Anyone who wants to trade currencies has to know who these brokers are and how they work.
What is a Forex Broker?
A forex broker is a financial services company that provides traders with access to a platform for buying and selling foreign currencies. In essence, they act as a gateway, connecting retail traders to the vast network of banks and financial institutions that make up the interbank market, where currency transactions occur.
Forex brokers cater to various clients, from individual retail traders to institutional investors, offering accounts with different leverage ratios, spreads, and minimum deposit requirements.
Types of Forex Brokers
When a trader wants to buy or sell a currency pair, like the EUR/USD, they place an order via the broker’s trading platform. After that, the broker carries out this order. How they do it depends on how their business works. There are two main types of forex brokers:
- Dealing Desk Brokers (or Market Makers): A dealing desk broker creates a market for their clients. Essentially, they do the opposite of what their clients want them to do. The market maker sells a currency pair to a trader who wants to buy it.
Similarly, the market maker will buy a trader’s assets when the latter want to sell. This means that the broker’s profit or loss is directly dependent on how well their clients trade.
The spread is the main way that market makers generate money. The “bid” is the price at which the broker is willing buy a currency, and the “ask” is the price at which they are willing to sell it.
The spread is the difference between these two prices. This difference is the broker’s fee for making the trade happen. For instance, if the bid price for EUR/USD is 1.0707 and the ask price is 1.0710, the spread is 3 pips. Quotes already include spreads. Also, they grow wider when the market is volatile, such as when a major news breaks. - No Dealing Desk (NDD) Brokers: Instead of trading against their clients, these brokers support them. They do this by going straight to the interbank market to get liquidity for their customers. There are two main types of NDD brokers:
- Straight Through Processing (STP): STP brokers forward their clients’ orders to one or more liquidity providers. They usually add a little fee to the spread they get from their liquidity providers.
- Electronic Communication Network (ECN): ECN brokers facilitate interactions between traders and other network participants like as banks, hedge funds, and other traders. This setup has tighter spreads and is more transparent, but it usually needs larger deposits.
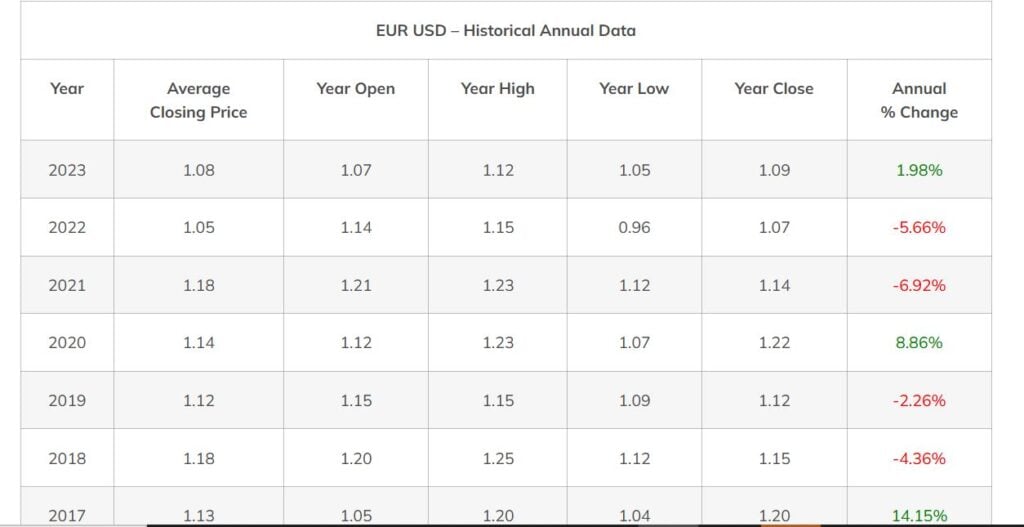
EURUSD Historical data since 2017. Source: ATFX
How Do Brokers Make Money?
Forex brokers make money in a few main ways:
- Spreads: This is the most popular way. For instance, the spread is 2 pips if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.1005/1.1010. This is the broker’s profit margin.
- Commissions: Some brokers charge a modest fee for each trade, usually on ECN accounts.
- Swaps (Overnight Fees): If a position is kept overnight, brokers may charge or pay interest based on the currencies involved and the outcome of the trade.
- Premium Services: Some brokers charge extra for items like analytical tools, trading signals, or premium account types.
Regulation of Brokers
Regulation of Brokers Safety is very important. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA) watch over brokers in the U.S. They require that client funds be kept separate and that losses don’t go beyond deposits.
The UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), Australia’s ASIC, and Cyprus’s CySEC all provide Tier-1 control around the world. They all require audits and capital reserves. Unregulated brokers can be risky because they can commit fraud or mismanage funds. Always check with resources like the NFA’s BASIC database.
In Summary
In conclusion, forex brokers connect customers to the trillion-dollar forex market by using technology, liquidity, and leverage to make trading currencies possible for everyone. They work behind the scenes to make trades and manage risks, but individual trader success depends on making smart decisions and sticking to a plan.
A forex broker acts as an intermediary, giving traders a platform and access to the foreign exchange market to buy and sell currencies.
The two main types are Dealing Desks (also called market makers) who sell and buy currency pairs directly to traders and No Dealing Desk brokers, who link trades directly to the interbank market.
Regulation via bodies like CFTC or FCA ensures client fund safety, transparency, and loss protection.


